Your project management tool will become your communication hub and command center for your entire team for the life of your project. It's important to pick the right one.
In this article, I'll outline six steps that will help you make an informed decision in selecting the best project management tools that will transform the way you manage projects and that will lead to more efficient and successful outcomes.
6 Steps To Choose The Right Tool
The following sections describe what I believe are six core steps you have to go through when selecting the best project management solution. If you don’t go through these steps, you risk investing in a tool with scalability limitations, lack of support for the project methodology you are using, or pricing that you cannot cover in the long run.
Step 1: Define Your Business Needs
The first thing you need to do is take a step back and analyze your business needs. A cloud-based solution is great for teams that need to be aligned in real-time, receive notifications to take action, and follow project progress at all times. However, some organizations have work that is more siloed, does not require much interaction, and could be solved using other tools.
The following situations might indicate a problem that you can address with cloud-based project management platforms:
- Lack of communication between teams (misaligned teams)
- Disorganized project management and missed deadlines
- Inability to gain insights from customer feedback
- Poor time tracking leading to uneven workload between teams
- Team collaboration happening through email
- Too many unproductive meetings
By identifying your business needs, you can start to rule out tools that don't fit the bill. This will leave you with a smaller pool of options that are better suited for your projects.
Step 2: Consider Your Team's Needs
The next step is to think about your team and what they need from a project management tool. Do they prefer something simple and straightforward? Or do they need robust features and customization options?
You'll also want to consider how big your team is and if you need a tool that can accommodate a large number of users. Additionally, think about where your team is located. If you have team members working remotely, you'll need a collaboration tool that makes it easy to stay connected and collaborate no matter where they are.
Step 3: Determine Your Budget
Your budget is an important factor to consider when choosing a project management tool. There is a wide range of options available, from free tools for small teams to enterprise-level solutions, so it's important to know how much you're willing to spend.
Don't forget to consider the long-term costs of a tool as well. Some tools may have a lower upfront cost but require a subscription or additional fees for features that are essential for your project. However, the long-term costs of a tool also include growth projections for your PMO. By considering your budget and what you're willing to pay, you can further narrow down your options.
Step 4: Consider Integration and Ease of Use
Once you've determined your business needs, what your team wants, and what your budget is, it's time to start evaluating specific tools. As you look at different options, pay attention to their user interface and how easy it is to navigate.
You'll also want to consider how user-friendly the interface is. A tool with a complex interface may steepen the tool's learning curve, which can impact productivity and slow down your project.
Additionally, integrations will impact the use of a tool as pre-built connections to a CRM, file sharing, or messaging platform can significantly decrease the time spent on switching between apps.
Step 5: Evaluate Features and Functionality
Now that you've considered the basics, it's time to start evaluating specific features and functionality. When looking at different tools, pay attention to features that are essential for your project and compare them side-by-side. With a range of features, automations, and customization, it's important to narrow down your choices by determining what your needs are and how to meet them with the right tool. This will help you select the right project management software.
Some common project management features to look for include:
- Task management (tasks, subtasks, and dependencies)
- Progress tracking (due dates, milestones, and deliverables)
- Resource management (workload, utilization, and allocation)
- Budgeting
- Visual project planning
- Reporting and analytics
Step 6: Try Before You Buy
The final step is to try out the tools you're considering. Even if you are going for a monday.com or a ClickUp which has tons of documentation, videos, and demos. Most project management tools offer a free trial so you can test them out before making a commitment. This is an important step because it allows you to see how the tool works in your work scenarios and if it's a good fit for your team.
For some more tips on this, listen to my chat with Olivia Montgomery about getting the most out of your software demos and trials here!
Need expert help selecting the right Project Management Tool?
If you’re struggling to choose the right software, let us help you. Just share your needs in the form below and you’ll get free access to our dedicated software advisors who match and connect you with the best vendors for your needs.
What Types of Software Tools Do Project Managers Use?
Project managers use different types of software tools to help them plan, execute, and track projects. These tools can be divided into several categories, including project management software, resource management software, task management software, Gantt chart makers, digital asset management software, and agile tools.
Project Management Software
Project management software is the most common type of tool used by project managers. This type of software includes features for task management, resource management, progress tracking, budgeting, and reporting. Common examples of project management software include Asana, Trello, Basecamp, and Jira.
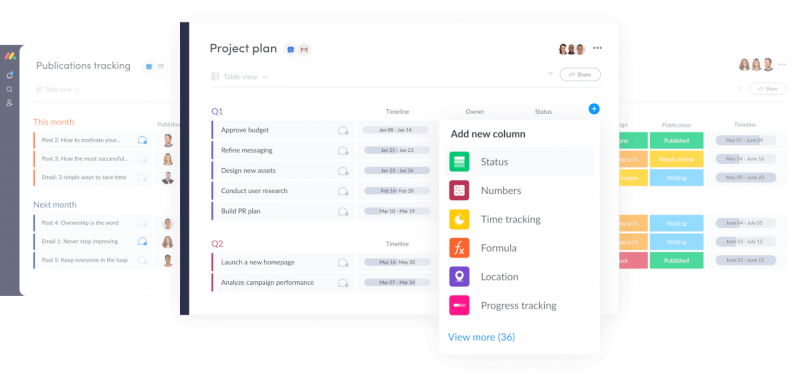
Resource Management Software
Resource management software is another tool that project managers often use. This type of software helps them to track and allocate resources, such as human resources, equipment, and materials. It can also be used to schedule tasks and monitor utilization rates. Common examples of resource management software include Smartsheet and Microsoft Project.
Learn more about choosing the right resource management software here.
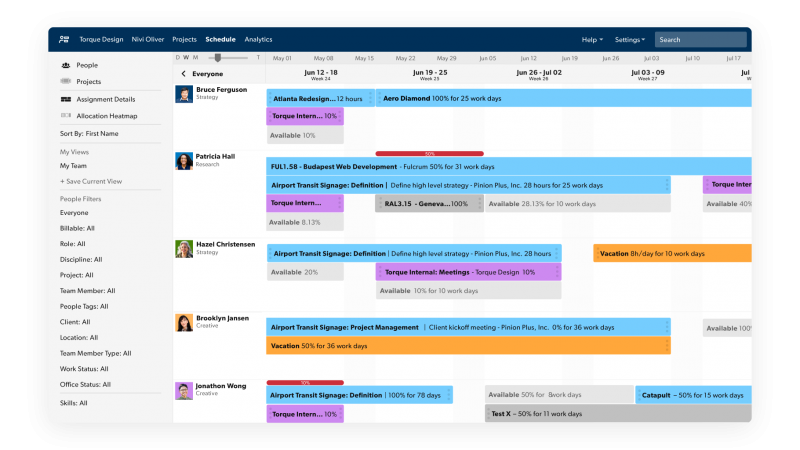
Task Management Software
Task management software is another tool that project managers might use to plan and track tasks. This type of software includes features for creating task lists, assigning tasks to team members, setting deadlines, and tracking progress. Common examples of task management software include Todoist and Wrike.
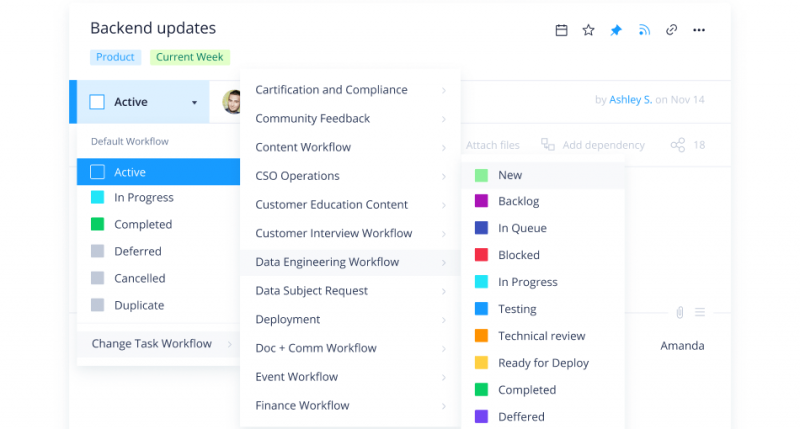
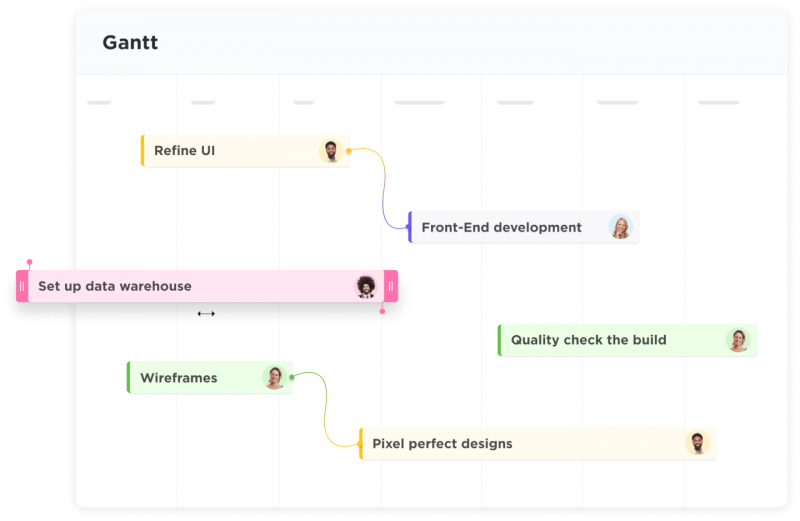
Gantt Chart Makers
Gantt chart makers are another type of tool that project managers use. This type of software helps them to create visual representations of their projects, including timelines, Gantt charts, and schedules. Common examples of Gantt chart makers include Microsoft Project and Smartsheet.
Learn more about Gantt chart software here.
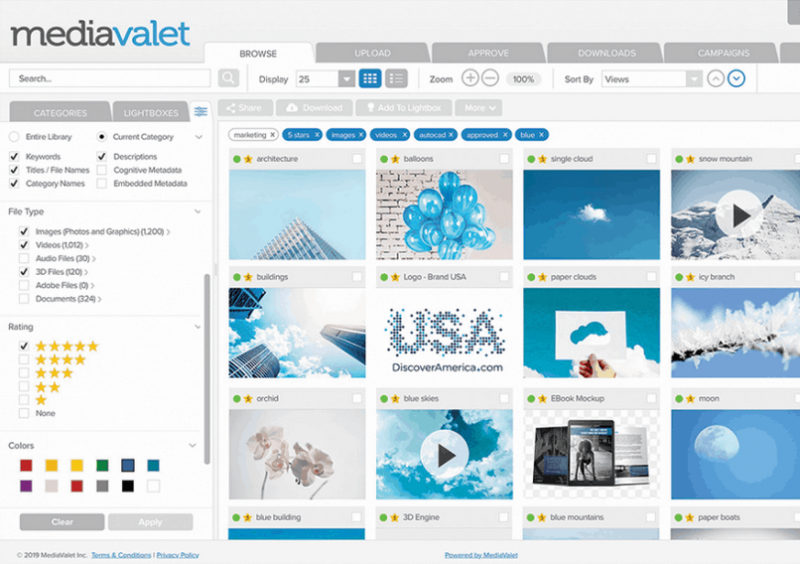
Digital Asset Management Software
Digital asset management software is another tool that project managers use to store and track digital assets. This type of software helps them to organize files, such as images, videos, and documents. Common examples of digital asset management software include Adobe Creative Cloud and Dropbox.
Agile Tools
Agile tools are another type of software that project managers use. This type of software helps them to plan and track agile projects. Common examples of agile tools include Jira, Trello, and Asana.

Get Started Using PM Software
By following these steps, you can be sure to find the best project management tool for your needs. From small businesses to enterprises, with the right tool in place, companies can streamline their workflow, improve communication and collaboration, and keep projects on track from start to finish.
Ready to get started? Check out our buyer's guide for choosing project management software to help narrow down your choices, and read more about the use cases of project management software here.
And if you’d like to stay up to date with the latest best practices for project managers, subscribe to our newsletter to make sure you never miss a beat.