A clear and detailed risk management plan helps you assess the impact of project risks and understand the potential outcomes of your decisions. It can be a useful tool to support decision making in the face of uncertainty.
However, I have seen projects fail because stakeholders did not take the risk management plan seriously or because the project failed to implement a risk management strategy.
Read on to learn how you can avoid these mistakes for your projects.
What Is A Risk Management Plan?
A risk management plan, or RMP, is a document describing how your project team will monitor and respond to unexpected or uncertain events that could impact the project.
The risk management plan:
- analyzes the potential risks that exist in your organization or project
- identifies how you will respond to those risks if they arise
- assigns a responsible person to monitor each risk and take action, if needed.
Team members and stakeholders should collaborate to create a risk management plan after starting to develop a project management plan but before the project begins.
What’s Covered In A Risk Management Plan?
The fidelity of your risk management plan will vary depending on the nature of your project and the standard operating procedures that your organization uses.
A project risk management plan seeks to answer:
- What is this project, and why does it matter?
- Why is risk management important for the project’s success?
- What will the team do to identify, log, assess, and monitor risks throughout the project?
- What categories of risk will we manage?
- What methodology will be used for risk identification and to evaluate risk severity?
- What is expected of the people who own the risks?
- How much risk is too much risk?
- What are the risks, and what are we going to do about them?
Depending on the project, this document could be hundreds of pages—or it could be less than a dozen. So how do you decide how much detail to provide? Here are two illustrative examples (but by no means are they the only ways to do it!).
PS. If you’re looking for additional information, we also did a workshop on managing risk that’s available for DPM members.
2 Types Of Risk Management Plans
In this section, we’ll cover 2 common types of risk management plans—a RAID log and a risk matrix.
#1: Simpler Version—Lightweight RAID Log
In its most minimal form, a risk management plan could be a handful of pages describing:
- how and when to assess risk
- the roles and responsibilities for risk owners
- at what point the project risk should trigger an escalation.

Instead of a formal risk register designed to calculate risk severity, a lightweight risk management approach may simply involve maintaining a risk list in your weekly status report.
This list (also known as a RAID log) tracks risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies so that the project team and sponsor can review and further discuss.
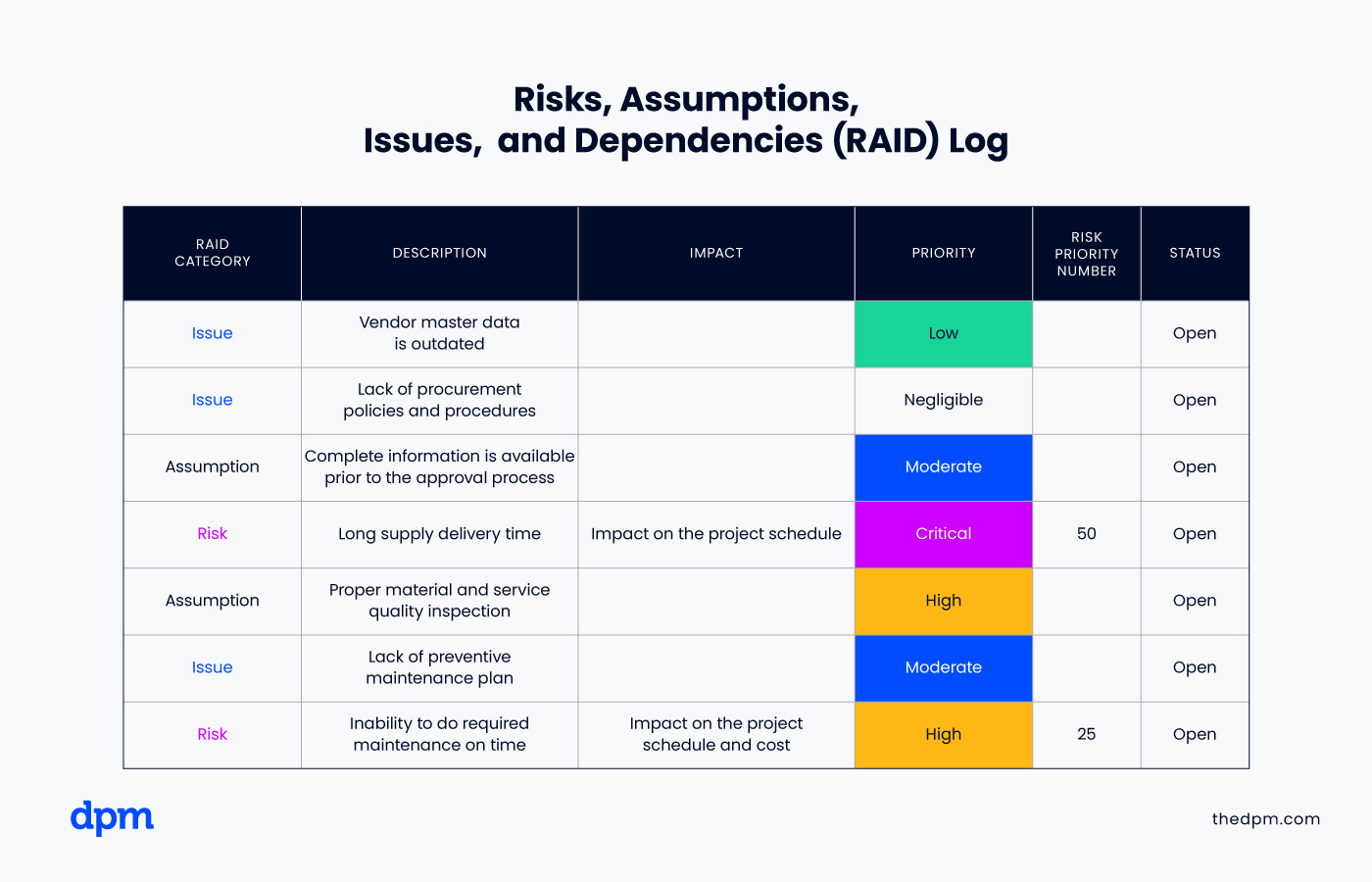
When to use it: this approach could be useful for a small non-technical project being executed by a team of 3-4 people in an organization that does not have a standard approach to risk management.
#2: Complex Version—Risk Matrix
When an organization already has a culture of risk management, there may be a template to follow that demands a high level of detail. These details may include a full description of the methodology that the organization will follow to perform qualitative and quantitative risk analysis, along with an impact matrix.
An impact matrix, or risk assessment matrix, shows the relationship between risk factors in calculating risk severity. Risks that are high-probability and high-impact are the most severe.
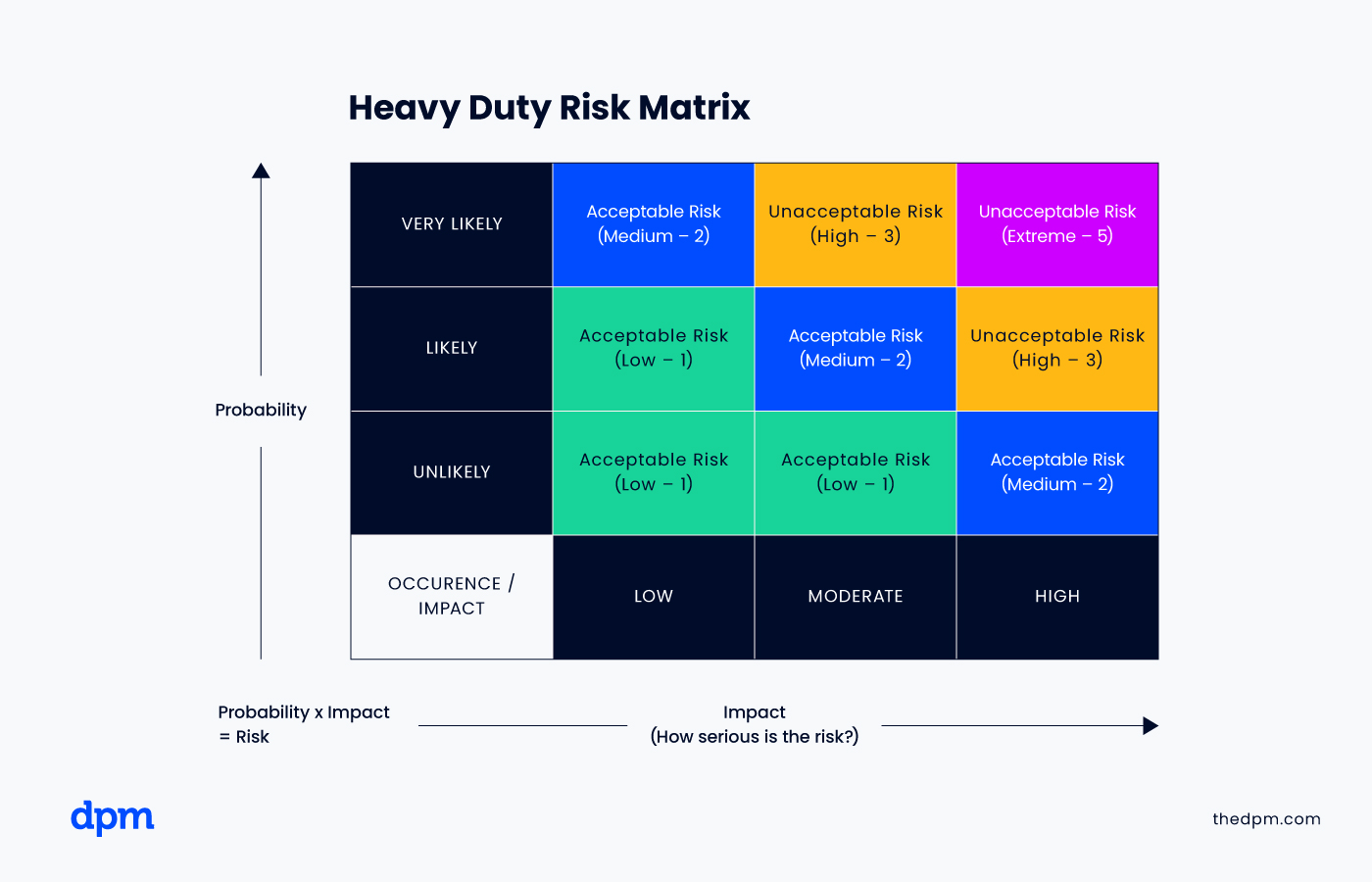
An organization may design its risk register template to prioritize and assign a numerical severity score to measure the level of risk.
Additionally, you may need to create a risk breakdown structure to decompose higher-level risk categories into smaller, more specific risk subcategories
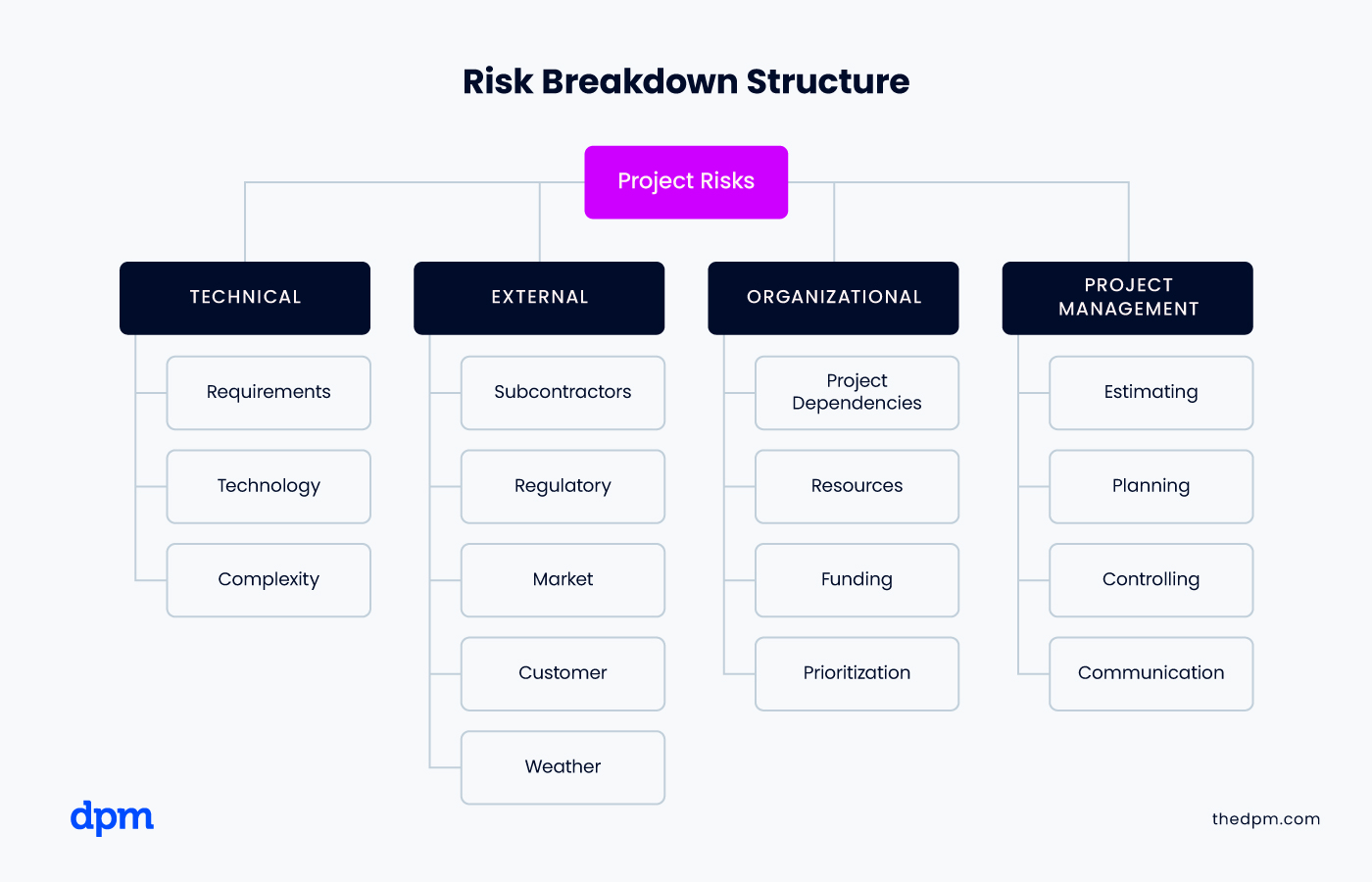
When to use it: making a detailed risk management plan isn’t about creating complexity for complexity’s sake—you and your team will be glad to have this level of detail on a large enterprise project that involves larger teams, multiple stakeholders, and high stakes that could have a significant impact on the business.
In terms of tooling, there are some great options available for managing risk on your project. Many organizations favor spreadsheets as part of an enterprise business software bundle, but there are also some providers that support risk management planning specifically.
Two examples of risk management software are Wrike and monday.com. These tools integrate the entire risk management process with the wider project management plan.
The most important consideration is not the tool used, but rather the discussions you’ll have with your team and your project sponsor about how to navigate risks to increase the likelihood of project success.
How To Make A Risk Management Plan
Below is a step-by-step guide to developing your own version of a risk management plan. Keep in mind that the nature of these steps may vary depending on the type of project involved, so don’t be afraid to tailor these steps to meet project and organizational needs.
1. Prepare supporting documentation
You’ll want to review existing project management documentation to help you craft your risk management plan. This documentation includes:
- Project Charter: among other things, this document establishes the project objectives, the project sponsor, and you as the project manager. Frankly, it gives you the right to create a project management plan and then a risk management plan within that. If formal project charters aren’t used at your organization, you should at least have this documented in an email or a less formal brief.
- Project Management Plan: not to be confused with the project plan, this document outlines how you’ll manage, monitor, and control your project, including what methodology to use, how to report progress, how to escalate issues, etc. Your risk management plan should act as a subcomponent of the project management plan.
- Stakeholder Register: it’s good to have a solid idea of who the project stakeholders are before assessing risk. Each of these stakeholder groups presents a different set of risks when it comes to people, processes, and technology. You can also invite stakeholders to identify risks throughout the project and even nominate them as risk owners!
2. Set the context
Once you have your supporting documentation available, use it to frame up the discussion around your risk management plan. Specifically, take the project description and objectives from the project charter and use them to outline the business value of the project and the negative impacts that would result should the project fail.
The introduction to your risk management plan should explain the intent of this document and its relationship to the overarching project management plan. Use this context to drive a conversation about risk management with your team and your project sponsor.
3. Decide with your team how to identify and assess risks
Different methodologies are appropriate for different types of projects. The methods you choose also need to be sustainable for the team to perform throughout the project.
The key here is to have the right discussions and gather input to build consensus with your team and your stakeholders early in the project life cycle. Use these discussions to agree on risk categories, risk response plans, and ways to calculate risk severity.
4. Continuously identify risks
Once you’ve decided on the methodology to use, now the real fun begins—thinking about the things that could go astray during your project!
A great way to do this is to hold a risk workshop—a group session involving your team, key stakeholders, project sponsor, and subject matter experts to identify, evaluate, and plan responses to risks.
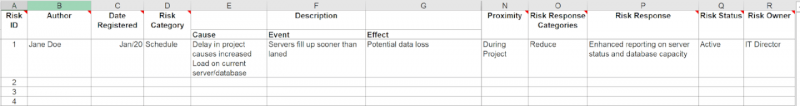
In the example below, I have used a simple overview from a sample project. During the workshop, you’d discuss everything in columns E-R and make sure that you have clear, SMART outcomes to put in each of the boxes. (SMART stands for specific, measurable, action-oriented, realistic, and timebound.)
I like to keep a copy of the risk register on my desk during the workshop to make sure that each column is discussed and populated appropriately. After the workshop, add any supporting details to finalize the document.
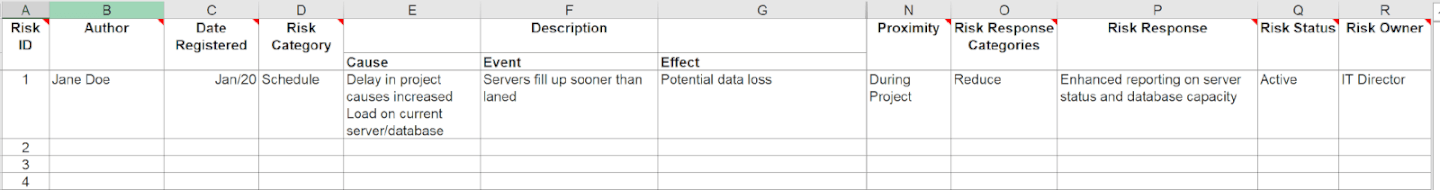
The project manager’s role during a risk workshop is to facilitate the meeting effectively. This involves brainstorming with stakeholders to evaluate both known risks and possible risks that may not have been considered. It could look something like this:

At the end of the workshop, your goal is to come away with stakeholder alignment on project risks, the desired risk response, and the expected impact of the risks. Stakeholder buy-in is critical for a successful risk response, so time in the workshop is likely to be time well-spent.
5. Assign risk owners
As you identify risks, you should work with the team to assign owners (including yourself). Project managers are responsible for risk management too!
That being said, the project manager can’t own everything. Assigning risk owners can be the most difficult area of risk management to finalize because it requires stakeholder accountability.
Make sure that risk owners have reviewed the risk management plan and are clear on their responsibilities. Follow up with them as you monitor risk throughout the project life cycle.
6. Populate the risk register
Following the risk workshop, finish populating any information required for the risk register. This includes a description of the risk, the risk response category, detailed risk response, risk status, and risk owner.
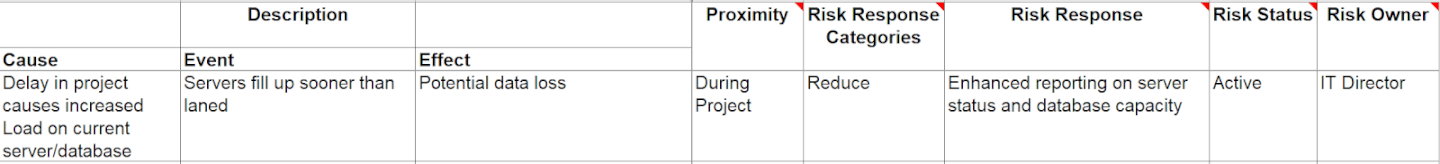
What’s important to remember during this exercise is ensuring that the risk response reflects the severity and importance of the risk. You can then review the broader risk register to understand any wider correlations that might exist among risks.
7. Publish the risk register
Send around the updated risk register within 48 hours of the workshop to give everyone time to read and process the output.
You can also use the risk register within wider project discussions to explain or define the timeline for a project or specific actions that need to be completed. It’s important to be timely so that the output can be used in other project artifacts.
8. Monitor and assess risks continuously throughout the project
New risks are introduced to a project constantly. In fact, mitigating one risk might create another risk or leave “residual risk.”
If feasible within your project constraints, try to run risk workshops periodically throughout the duration of the project or incorporate risk register reviews into other recurring planning activities.
Nothing feels quite as deflating as when you swerve to avoid one risk only to drive blindly into another, much bigger risk.
9. Archive your risk management plan in a reusable & accessible format
After your project, it’s a good idea to archive your risk management plan for future reference.
There are many reasons why (in fact, it may be mandatory in your organization), but here’s the main one: while not every risk management plan suits every project, the risk and response strategies may remain applicable. Use past risks to create a foundation for your next project.
Examples Of Risk Management Plans In Action
Admittedly, the word “risk” is itself a bit broad. Not having enough resources to hit the project deadline is a risk. Hurricane season is a risk. Disruption of the space-time continuum is a risk.
So, where do you draw the line on what types of risks to consider—which risks have a large enough potential impact to require attention, or even a contingency plan?
Here’s one way to think about it:
If the item is related to people, processes, resources, or technology and has any likelihood of threatening project success, you should log it as a risk.
Now, you might not need to do a comprehensive analysis on every risk in your risk register, but you do need to revisit the risks identified and conduct risk monitoring throughout the project. If someone starts testing a time machine near your office, for example, your highly unlikely space-time continuum risk has escalated.
Does this matter?
Yes. To prove it, here’s a simple example of risk management that saved a project:
A colleague was working on a service design project that required in-person research (this was before COVID-19), and on her RACI chart, she had clearly communicated to the client that it was the client’s responsibility to book a meeting space to conduct this research. She had logged a risk with her team that the client might not be able to secure a space.
Two days before the research commenced, the client informed her they weren’t able to secure the space. Luckily, her risk mitigation strategy on this particular risk was to book a backup space at the office, which she had done weeks ago.
Something that could have stalled the project for weeks had become nothing more than an email that said something like “All good, we’ll use our space."

Here’s another example:
An agency agreed to an aggressive timeline for a highly technical project. The team had raised concerns as the project was being initiated, but leadership still wanted to proceed. The project manager and technical architect logged the timeline risk before the project started, and their risk response strategy was to re-evaluate the project timeline using a Monte Carlo simulation.
After calculating a pessimistic, optimistic, and likely duration for every project activity on the critical path, they determined mathematically that the project had a 3% chance of hitting the deadline.
The project manager raised this with the client, and the client agreed to re-scope the project and re-baseline the project before getting going. It was too big of a risk for them to take.

Risk Register Template
There are a lot of risk register templates available online, and I would recommend looking at one that fits your needs, rather than one that includes every possible scenario.
In the risk management plan template available in DPM Membership, we’ve tried to keep the risk register as simple as possible to ensure that you’re able to enter the relevant information for your project.


Best Practices For Risk Management Plans
Consider these best practices to help you craft an effective risk management plan:
- Develop the risk management plan during the project planning phase, after you’ve developed the project charter and the project management plan, to give stakeholders the necessary context
- Adapt the format and level of detail of the risk management plan to align with the needs of the project, industry, and organization that you support
- Assign a risk owner to every risk identified in your risk register, and hold them accountable for the risk response
- Continuously identify risks throughout the project life cycle and update the risk register accordingly
- During project closing, archive your risk management plan and use it to inform risk planning on future projects.
What Do You Think?
Whether you’re a novice project manager or a seasoned pro, having a good risk management plan is vital to project success. And, the key to a successful risk management plan is adaptability.
You need to make sure that, with every project you run, you can adapt the risk management plan to your project, industry, and organization.
If you’ve got a great story about a risk you mitigated successfully on your project or a different way to manage risk, please share it in the comments below!






